In the realm of scientific exploration and technological advancements, precision and accuracy reign supreme. Amidst this meticulous pursuit, two tenths of a milligram emerges as a unit of measurement that carries immense weight, shaping our understanding of the world around us.
Two tenths of a milligram, a minuscule quantity that may seem inconsequential at first glance, plays a pivotal role in various scientific disciplines, from chemistry and biology to engineering and medicine. As we delve into the intricacies of this seemingly insignificant unit, we will uncover its profound implications and the fascinating applications where it holds sway.
Units of Measurement
The metric system is an internationally recognized system of measurement based on the decimal system. It is used in most countries around the world for scientific, engineering, and commercial purposes. The metric system is based on seven base units, which are the meter, kilogram, second, ampere, kelvin, mole, and candela.
These base units are used to derive other units of measurement.Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. The base unit of mass in the metric system is the kilogram (kg). Other units of mass include the gram (g), which is one-thousandth of a kilogram, and the milligram (mg), which is one-thousandth of a gram.The
following table shows the conversions between milligrams and other units of mass:| Unit | Conversion ||—|—|| Milligram (mg) | 1 || Gram (g) | 1,000 || Kilogram (kg) | 1,000,000 || Ounce (oz) | 28,349.5 || Pound (lb) | 453,592 |
Decimal Notation: Two Tenths Of A Milligram

Decimal notation is a way of writing numbers that uses a decimal point to separate the whole number part from the fractional part. The decimal point is a period (.) placed on the line of the number.
To convert a fraction to a decimal, divide the numerator by the denominator. The decimal point will be placed after the whole number part of the answer.
Converting Two Tenths of a Milligram to Decimal Notation
To convert two tenths of a milligram to decimal notation, we divide 2 by 10:
“`
÷ 10 = 0.2
“`
Therefore, two tenths of a milligram is equal to 0.2 in decimal notation.
Two tenths of a milligram is a very small amount, but it can still have a significant impact. For example, it is the amount of caffeine in a single cup of coffee. Or, it is the amount of nicotine in a single cigarette.
And, it is the amount of lead that is allowed in a gallon of gasoline. As you can see, two tenths of a milligram can be found in many different places, and it can have a variety of effects. Jack on 30 Rock Crossword is a fun and challenging puzzle that can help you learn more about two tenths of a milligram and its many uses.
Significant Figures

Significant figures are digits in a measurement that are known with certainty and are used to indicate the precision of the measurement. They are important in scientific measurements because they allow us to compare the accuracy of different measurements and to determine the uncertainty in a measurement.
Determining Significant Figures
The number of significant figures in a measurement is determined by the following rules:
- All non-zero digits are significant.
- Zeroes between non-zero digits are significant.
- Trailing zeroes after a decimal point are significant.
- Leading zeroes before a non-zero digit are not significant.
Significant Figures in Two Tenths of a Milligram
Two tenths of a milligram is written as 0.2 mg. According to the rules above, there are two significant figures in this measurement: the 2 and the 0 after the decimal point. The leading zero before the decimal point is not significant.
Potential Sources of Error When Measuring Small Quantities
When measuring small quantities, there are several potential sources of error that can affect the number of significant figures in the measurement. These include:
- The precision of the measuring instrument
- The skill of the person making the measurement
- Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity
It is important to be aware of these potential sources of error when making scientific measurements and to take steps to minimize their impact.
Precision and Accuracy
Precision and accuracy are two important concepts in scientific measurements. Precision refers to the closeness of a set of measurements to each other, while accuracy refers to the closeness of a measurement to the true value. In other words, precision tells us how consistent our measurements are, while accuracy tells us how close we are to the bullseye.
The number of significant figures in a measurement affects its precision. The more significant figures a measurement has, the more precise it is. For example, a measurement of 12.34 has three significant figures and is more precise than a measurement of 12, which has only two significant figures.
Factors that Affect Accuracy
There are a number of factors that can affect the accuracy of a measurement. These include:
- The quality of the measuring instrument
- The skill of the person making the measurement
- The environmental conditions under which the measurement is made
It is important to be aware of these factors when making scientific measurements, so that we can take steps to minimize their impact on the accuracy of our results.
Applications
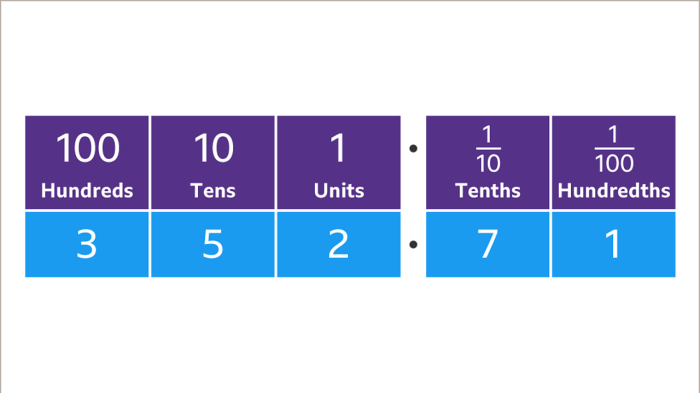
Two tenths of a milligram (0.2 mg) is a small but significant measurement used in various scientific and technological fields.
Precision and accuracy are crucial in these applications as they determine the reliability and validity of the measurements.
Medicine, Two tenths of a milligram
- Dosage of medications: Precise measurement of drug doses is essential to ensure the safety and effectiveness of treatments. For example, in cancer chemotherapy, accurate dosing of cytotoxic drugs is critical to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing side effects.
- Drug testing: In clinical trials and drug development, precise measurements of drug concentrations in blood or tissue samples are necessary to determine the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug and its potential efficacy and toxicity.
Environmental Science
- Water quality monitoring: Measurement of trace contaminants, such as heavy metals or pesticides, in water samples at the 0.2 mg level can help assess the health of aquatic ecosystems and protect human health.
- Air pollution monitoring: Precise measurements of particulate matter and other pollutants in the air at this level can provide valuable data for understanding air quality and its impact on human health and the environment.
Nanotechnology
- Nanomaterial characterization: The precise measurement of the size and properties of nanoparticles is essential for understanding their behavior and potential applications in various fields, including electronics, optics, and medicine.
- Drug delivery: Precise control over the size and dosage of drug-loaded nanoparticles is crucial for targeted drug delivery and improved therapeutic outcomes.
Essential FAQs
What is the metric system?
The metric system is a standardized system of measurement based on the decimal system, providing a coherent and convenient framework for quantifying physical quantities.
How do I convert two tenths of a milligram to decimal notation?
To convert two tenths of a milligram to decimal notation, divide 2 by 10, resulting in 0.2 mg.
What is the difference between precision and accuracy?
Precision refers to the closeness of multiple measurements to each other, while accuracy measures how close a measurement is to the true value.