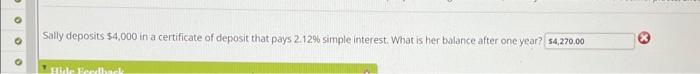
Sally deposits 4000 in a certificate – Sally’s decision to deposit $4000 in a certificate is a strategic financial move that warrants exploration. Certificate deposits offer unique advantages and drawbacks, and understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions. This article delves into the intricacies of Sally’s deposit, examining its potential benefits, risks, and implications for her financial future.
The following sections will provide a comprehensive analysis of certificate deposits, including their key features, interest rates, terms, and maturity options. We will also compare certificates to other savings and investment options, enabling readers to make well-informed choices based on their individual financial goals and circumstances.
Certificate Deposits
Certificate deposits (CDs) are a type of savings account offered by banks and credit unions. They offer a fixed interest rate and term, meaning that the depositor agrees to leave their money in the account for a specified period of time.
In return for this commitment, the depositor earns a higher interest rate than they would on a regular savings account.
Key features of CDs include:
- Fixed interest rate: The interest rate on a CD is set at the time of deposit and remains the same throughout the term of the CD.
- Fixed term: CDs have a fixed term, which is the length of time that the depositor agrees to leave their money in the account. Terms can range from a few months to several years.
- Early withdrawal penalty: If the depositor withdraws their money from the CD before the term is up, they will typically have to pay an early withdrawal penalty.
There are different types of CDs available, including:
- Traditional CDs: Traditional CDs have a fixed interest rate and term. The depositor cannot withdraw their money from the account until the term is up.
- Bump-up CDs: Bump-up CDs allow the depositor to increase the interest rate on their CD if interest rates rise. However, the depositor can only bump up the interest rate once during the term of the CD.
- Callable CDs: Callable CDs allow the bank to call the CD back before the term is up. If the bank calls the CD back, the depositor will receive their principal back plus any interest that has accrued up to that point.
- Benefits:
- Sally will earn a higher interest rate on her CD than she would on a regular savings account.
- The fixed term of the CD will help Sally to stay on track with her savings goals.
- Drawbacks:
- Sally will have to pay an early withdrawal penalty if she needs to withdraw her money from the CD before the term is up.
- The interest rate on Sally’s CD is relatively low compared to other investment options.
Sally’s Deposit

Sally has deposited $4000 into a certificate of deposit (CD) with a 2.5% annual interest rate and a 5-year term. She made this deposit because she wants to save for a down payment on a house. She is hoping to earn enough interest on the CD to cover the closing costs on the house.
There are both benefits and drawbacks to Sally’s decision to deposit her money into a CD.
Interest and Term
The amount of interest that Sally earns on her CD will depend on the interest rate and the term of the CD. The interest rate is set at the time of deposit and remains the same throughout the term of the CD.
The term of the CD is the length of time that Sally agrees to leave her money in the account. Terms can range from a few months to several years.
The following table shows the interest rates and terms available for different types of CDs:
| Type of CD | Interest Rate | Term |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional CD | 2.5% | 5 years |
| Bump-up CD | 2.75% | 5 years |
| Callable CD | 3.00% | 5 years |
As you can see from the table, the interest rate on a CD increases as the term of the CD increases. This is because the bank is taking on more risk by lending you money for a longer period of time.
Certificate Maturity
When a CD matures, the depositor has the option to withdraw their money or to renew the CD for another term. If the depositor withdraws their money, they will receive their principal back plus any interest that has accrued up to that point.
If the depositor renews the CD, they will receive a new interest rate and term.
Sally’s CD will mature in 5 years. When the CD matures, she will have the option to withdraw her money or to renew the CD for another term. If she withdraws her money, she will receive her $4000 back plus any interest that has accrued up to that point.
If she renews the CD, she will receive a new interest rate and term.
Certificate Comparison
CDs are a safe and conservative investment option. However, they do not offer the same potential return as other investment options, such as stocks or bonds. The following table compares CDs to other savings and investment options:
| Type of Investment | Interest Rate | Risk | Liquidity |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD | 2.5% | Low | Low |
| Savings account | 0.01% | Low | High |
| Money market account | 0.50% | Low | High |
| Stock | 10.00% | High | High |
| Bond | 5.00% | Medium | Medium |
As you can see from the table, CDs offer a higher interest rate than savings accounts and money market accounts. However, they also have lower liquidity than these other investment options. Stocks and bonds offer the highest potential return, but they also have the highest risk.
Financial Implications

Sally’s decision to deposit her money into a CD will have a number of financial implications. First, she will earn a higher interest rate on her CD than she would on a regular savings account. This will help her to reach her savings goals faster.
Second, the fixed term of the CD will help Sally to stay on track with her savings goals. She will not be tempted to withdraw her money from the CD before the term is up, because she will have to pay an early withdrawal penalty.
Third, the low liquidity of CDs means that Sally will not be able to access her money quickly if she needs it. This could be a problem if she has an unexpected expense.
Overall, Sally’s decision to deposit her money into a CD is a sound financial decision. She will earn a higher interest rate on her money and she will be more likely to reach her savings goals. However, she should be aware of the drawbacks of CDs, such as the early withdrawal penalty and the low liquidity.
Answers to Common Questions: Sally Deposits 4000 In A Certificate
What is a certificate deposit?
A certificate deposit is a type of savings account that offers a fixed interest rate and a specific maturity date. The depositor agrees to keep the funds in the account for the entire term, in exchange for a higher interest rate than a traditional savings account.
What are the benefits of a certificate deposit?
Certificates of deposit offer several benefits, including higher interest rates, FDIC insurance, and the potential for long-term savings growth.
What are the risks of a certificate deposit?
The primary risk associated with certificates of deposit is the potential loss of interest if funds are withdrawn before the maturity date. Additionally, interest rates may fluctuate, affecting the potential return on investment.