Quiz 3 1 parallel lines transversals and angles – Embark on an exploration of quiz 3.1, where we delve into the intriguing world of parallel lines, transversals, and angles. This module promises an immersive journey, unraveling the intricacies of these geometric concepts and their captivating applications.
Parallel lines, like steadfast companions, maintain an unwavering distance from each other. Transversals, like bold adventurers, cross these parallel paths, creating a tapestry of angles that reveal hidden relationships. Join us as we uncover the properties, theorems, and practical applications that govern these geometric entities, unlocking a deeper understanding of the world around us.
Parallel Lines, Transversals, and Angles
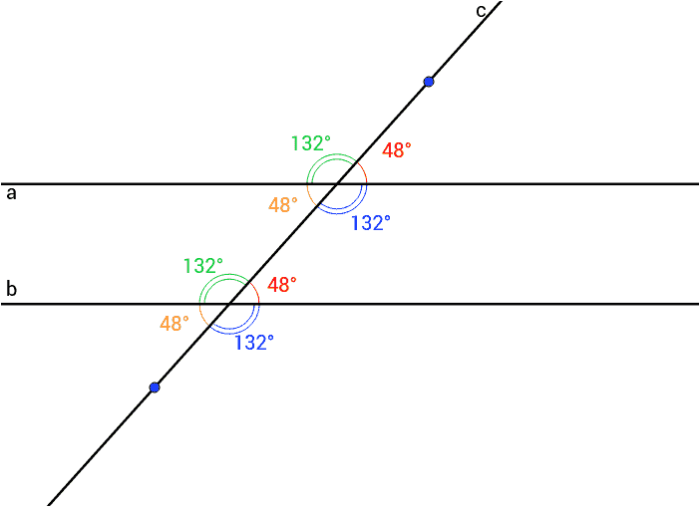
In geometry, parallel lines are two lines that never intersect, no matter how far they are extended. A transversal is a line that intersects two or more other lines.
When a transversal intersects two parallel lines, it creates eight different angles. These angles can be classified into four different types:
- Alternate interior angles: These are the angles that are on opposite sides of the transversal and inside the two parallel lines.
- Alternate exterior angles: These are the angles that are on opposite sides of the transversal and outside the two parallel lines.
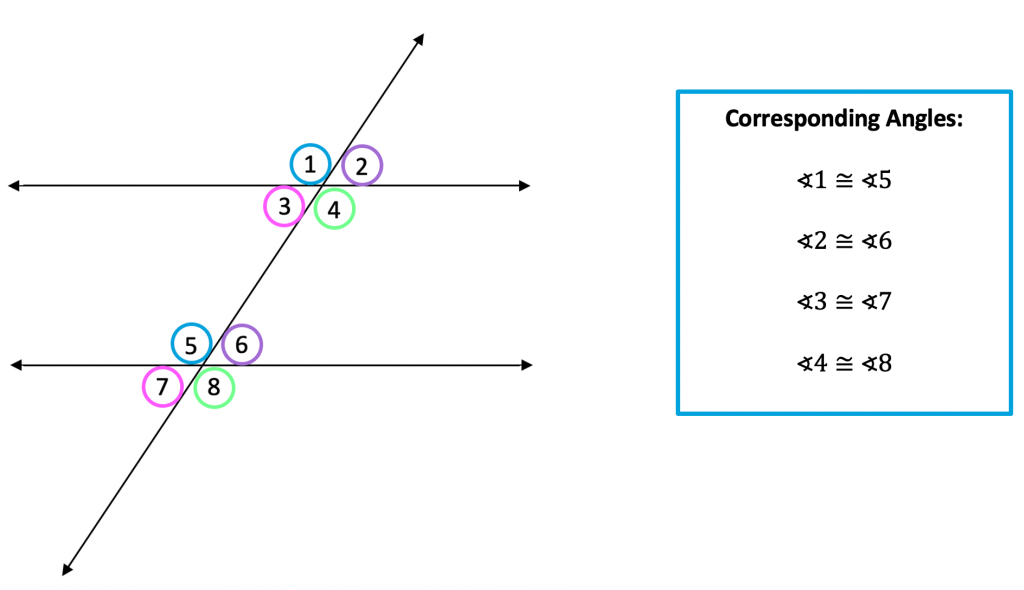
- Corresponding angles: These are the angles that are on the same side of the transversal and in the same position relative to the parallel lines.
- Vertical angles: These are the angles that are opposite each other and share a common vertex.
These angles have certain properties that can be used to solve geometry problems. For example, alternate interior angles are always congruent, and corresponding angles are always congruent.
Properties of Parallel Lines and Transversals
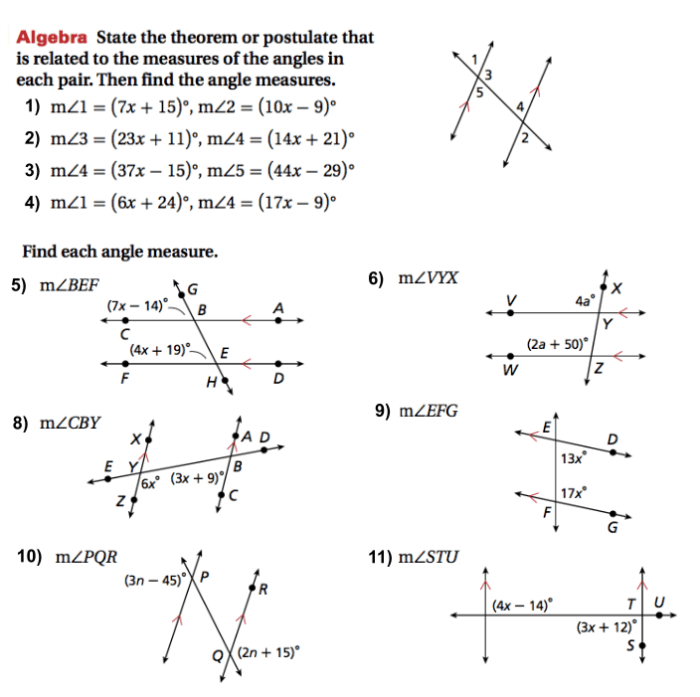
There are a number of properties that can be used to identify and use parallel lines and transversals. These properties include:
- If two lines are parallel to a third line, then they are parallel to each other.
- If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then the alternate interior angles are congruent.
- If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then the alternate exterior angles are congruent.
- If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then the corresponding angles are congruent.
- If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then the vertical angles are congruent.
These properties can be used to solve a variety of geometry problems. For example, they can be used to find the measure of an unknown angle, or to determine whether or not two lines are parallel.
Theorems Related to Parallel Lines and Transversals
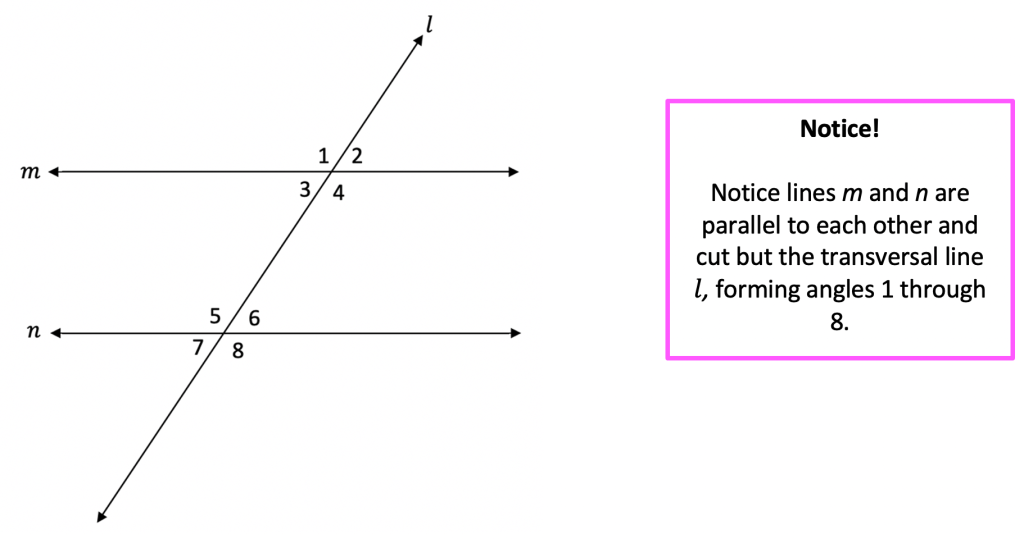
There are a number of theorems that are related to parallel lines and transversals. These theorems include:
- The Triangle Angle Sum Theorem: The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees.
- The Exterior Angle Theorem: The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two opposite interior angles.
- The Angle Bisector Theorem: If a line bisects an angle, then it divides the opposite side of the angle into two equal segments.
These theorems can be used to solve a variety of geometry problems. For example, they can be used to find the measure of an unknown angle, or to determine whether or not two lines are parallel.
Applications in Geometry: Quiz 3 1 Parallel Lines Transversals And Angles
Parallel lines and transversals are used in a variety of applications in geometry. These applications include:
- Architecture: Parallel lines are used to create the walls and roofs of buildings.
- Engineering: Parallel lines are used to create bridges and other structures.
- Surveying: Parallel lines are used to create maps and charts.
- Navigation: Parallel lines are used to create compasses and other navigational instruments.
These are just a few of the many applications of parallel lines and transversals in geometry.
Practice Problems
The following are a few practice problems that involve parallel lines, transversals, and angles:
- Find the measure of angle A in the following diagram:
- Determine whether or not the following lines are parallel:
- Find the value of x in the following diagram:



These are just a few examples of the many practice problems that can be used to assess understanding of parallel lines, transversals, and angles.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the key difference between parallel lines and transversals?
Parallel lines never intersect, while transversals intersect parallel lines at distinct points.
Can you explain the concept of alternate interior angles?
Alternate interior angles are non-adjacent angles that lie on opposite sides of the transversal and inside the parallel lines.
What is the significance of the Triangle Angle Sum Theorem in relation to parallel lines?
The Triangle Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. This theorem can be applied to triangles formed by transversals and parallel lines to solve for unknown angles.